DC Motor
Main content:
✔️ What is a DC motor?
✔️ Construction and classification of DC motors
✔️ Working principle of DC motor
✔️ DC Motor For Sale
✔️ Application of DC motor
What is a DC motor?
DC motors (DC stands for “Direct Current Motors”) belong to the class of induction motors, they are controlled by a current with a definite direction of “Direct Current.” Basically DC is extracted from DC Generator and Battery With these two types of power sources, DC Motor both receive and operate.
A direct current (DC) motor is a machine that implements the communication between electricity and magnetism based on the law of electromagnetic induction (by Faraday), for the purpose of generating kinetic energy.
DC motors today are not only appearing in civil, they are appearing more and more in industrial systems. For example, servo motor, stepper motor, etc.
 |
| A DC motor and its holder |
Note:
- The first DC motor was developed around 1830-1840, developed shortly after Fraraday discovered the law of electromagnetic induction in physics.
- Initially, the DC Motor was not commercially successful, because the main power supply was the Battery. But now the battery is extremely expensive but the quality is low.
- Until the alternating current (AC) grid created by Nikola Tesla, the battery, the rechargeable battery was developed, the DC motor was only commercialized and available on the market. To be more precise, the science of electronics in the early 20th century was very advanced, and they knew how to easily convert AC to DC to power DC motors.
Construction and classification of DC motors
- Stator: is one or more pairs of permanent magnets or electromagnets
- Rotor: the core is wound with coils to create an electrical and magnetic interface, to generate the rotational kinetic energy of the shaft.
- Brushes: keep contact and power for the commutator
- Commutator: is responsible for contacting and dividing the power supply for the windings on the rotor. The number of contacts will correspond to the number of windings on the rotor.
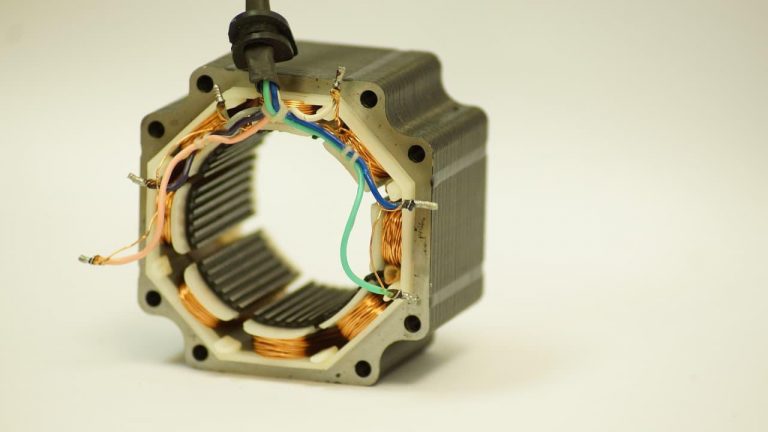 |
| The stator of the DC motor, in addition to the permanent magnet, can be combined with the coil to create an electromagnet. |
 |
| The wire is wound on the rotor of the DC motor in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic induction of the stator to get the maximum thrust. |
- DC motor with brush
- Brushless DC motor
Working principle of DC motor
 |
| Structure to show basic DC Motor working principle |
DC Motor For Sale
 |
| The untold variety of DC motors |
- 👉 FAR ALONG's DC motor
- 👉 VEVOR DC motor
- 👉 DC Motor Machinery CN
- 👉 DC motor of CNMALL CO (lots of brushless DC motors)
Application of DC motor
💠 Harnessing the power of back electromagnetic fields (Back EMF)
💠 Back EMF generates Lenz's Force in generator 💠 When the output energy is not affected by the Lenz (free) force, a self-powered mechanism will be established from the AC generator head to the induction motor. And the kinetic energy of the induction motor at that time was only supposed to stir the Ether by Nikola Tesla's "Rotating Magnetic Field". That's the mechanism for a Free Energy AC generator - no fuel needed - Self-powered generator.
AC generator without fuel: Simple Energy Hack KILLS Power Bills And Generates Power On Demand
Free Energy AC generator 👆



